What is the Difference Between XRF and LIBS?
EasyXrf.com – When it comes to understanding the materials around us, scientists and engineers use special tools to figure out what things are made of. Two popular tools for this are XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence) and LIBS (Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy).

What Are XRF and LIBS?
Before we dive into the differences, let’s first understand what these two tools are and what they do.
What is XRF?
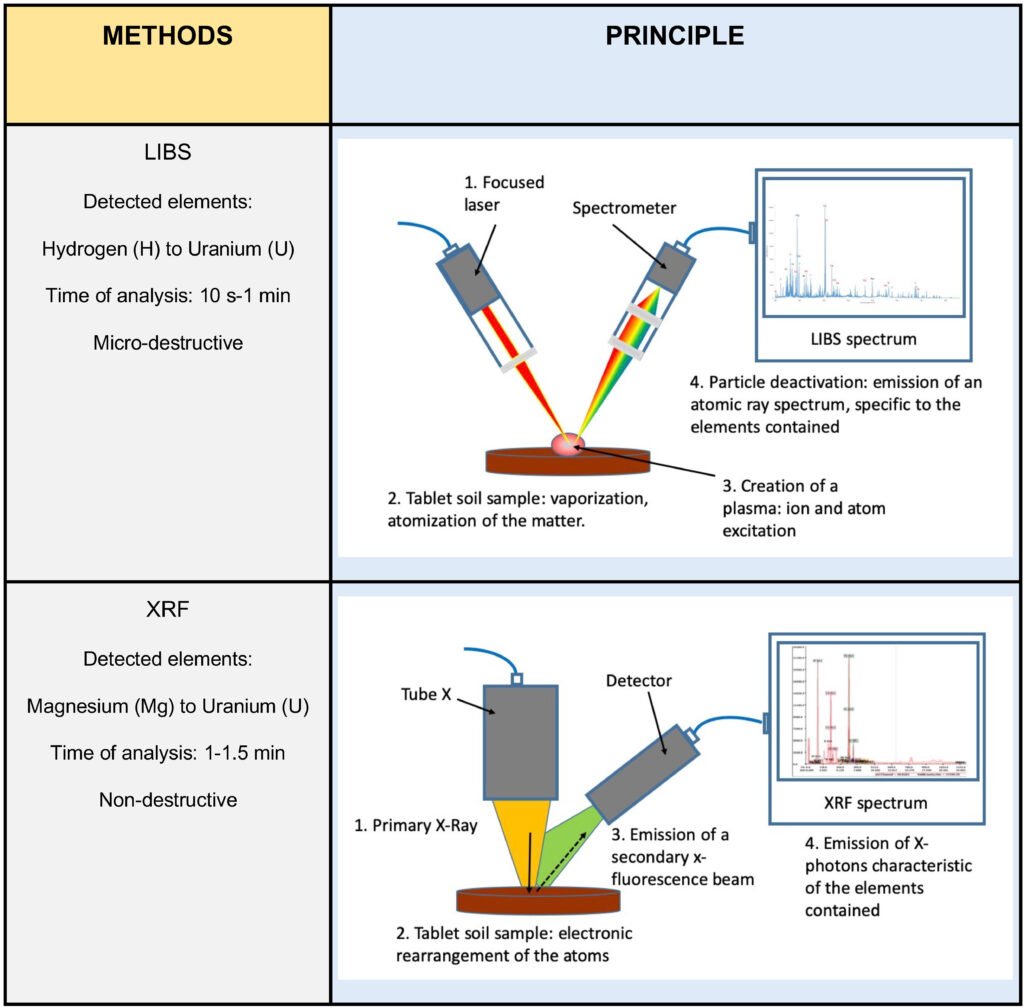
XRF, short for X-Ray Fluorescence, is a tool used to figure out what elements (like iron, gold, or oxygen) are inside a material. It works by shooting X-rays at the object. When the X-rays hit the object, the atoms inside it get excited and release their own X-rays. These released X-rays are like a fingerprint—they tell us what elements are present in the material.
For example, if you have a shiny piece of metal and want to know if it’s gold or just fake gold, XRF can help you find out!
What is LIBS?
LIBS stands for Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. This tool uses a laser beam to zap the surface of a material. The laser creates a tiny explosion (called plasma) on the surface, and this plasma gives off light. Scientists study the light to figure out what elements are in the material.
Imagine pointing a laser at a rock and seeing a rainbow of colors come out. Each color tells you something about the rock’s ingredients—like if it has iron, aluminum, or even rare elements like lithium.

How Do XRF and LIBS Work?
Now that we know what XRF and LIBS are, let’s look at how they work in more detail.
How Does XRF Work?
- X-Ray Beam: The device sends a beam of X-rays to the material.
- Excited Atoms: The X-rays excite the atoms in the material.
- Emission of X-Rays: The excited atoms release their own X-rays.
- Element Identification: The device reads the X-rays and identifies which elements are present.
Think of it like shining a flashlight on a mirror. The light bounces back, and you can tell what kind of mirror it is based on the way the light behaves.
How Does LIBS Work?
- Laser Beam: A high-powered laser hits the material.
- Plasma Formation: The laser creates a small plasma (a very hot, glowing gas).
- Light Emission: The plasma gives off light.
- Element Identification: The device analyzes the light to find out what elements are in the material.
It’s like using a magnifying glass to focus sunlight on a piece of paper. The paper burns, and the smoke tells you what the paper is made of.
Key Differences Between XRF and LIBS
Let’s compare XRF and LIBS side by side to see how they’re different.
1. The Type of Energy Used
- XRF uses X-rays to analyze materials.
- LIBS uses lasers to analyze materials.
2. Elements They Can Detect
- XRF is great for detecting heavier elements like iron, copper, and gold. However, it struggles with very light elements like lithium and hydrogen.
- LIBS can detect both heavy and light elements, including lithium, hydrogen, and even boron.
3. Speed
- Both XRF and LIBS are very fast, giving results in just a few seconds.
4. Damage to the Sample
- XRF is non-destructive, meaning it doesn’t damage the material being tested.
- LIBS is slightly destructive because the laser burns a tiny spot on the material.
5. Safety
- XRF uses X-rays, which are a type of radiation. This means users need to follow safety rules to avoid exposure.
- LIBS uses lasers, which can be dangerous to the eyes and skin if not handled properly.
Applications of XRF and LIBS
Both XRF and LIBS are used in many industries. Let’s explore some examples.
Where is XRF Used?
- Mining: To check what minerals are in rocks.
- Recycling: To sort metals like aluminum and copper.
- Jewelry: To test if gold or silver is real.
- Construction: To analyze cement and building materials.
Where is LIBS Used?
- Battery Production: To detect lithium in batteries.
- Aerospace: To check the quality of metals used in airplanes.
- Energy: To analyze materials in solar panels and wind turbines.
- Environment: To detect pollutants in soil and water.
Which One Should You Choose?
If you’re wondering which tool is better, the answer depends on what you need it for.
- Choose XRF if you’re working with metals and want a non-destructive test.
- Choose LIBS if you need to detect light elements like lithium or if you’re analyzing very small samples.
Sometimes, scientists even use both tools together for the best results!
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of XRF
- Non-destructive testing.
- Accurate for heavy elements.
- Easy to use.
Disadvantages of XRF
- Can’t detect light elements.
- Requires safety precautions due to X-rays.
Advantages of LIBS
- Can detect both heavy and light elements.
- Portable and fast.
- Works well for small samples.
Disadvantages of LIBS
- Slightly destructive.
- May require more training to use.
Fun Facts About XRF and LIBS
- XRF was first used in the 1950s and has been improving ever since.
- LIBS is inspired by how stars emit light. Scientists study starlight in a similar way to understand what stars are made of!
- Both tools are portable now, meaning you can carry them to a field or factory.
How Do These Tools Help the World?
XRF and LIBS are not just for scientists—they help make the world a better place!
- Saving Resources: By analyzing materials, we can recycle more efficiently and reduce waste.
- Protecting the Environment: LIBS can detect harmful pollutants in water and soil, helping us keep the planet clean.
- Creating Better Products: From smartphones to airplanes, these tools ensure that materials are high quality and safe to use.
Understanding XRF and LIBS
XRF and LIBS might sound like complicated tools, but they’re actually just ways to see what materials are made of. Whether it’s using X-rays or lasers, both tools help us in amazing ways—from recycling metals to building better batteries.
If you ever see a scientist or engineer using one of these tools, now you’ll know exactly what they’re doing!
By understanding the differences between XRF and LIBS, you can appreciate how technology helps us learn more about the world around us. Who knows? Maybe one day you’ll use these tools to make your own discoveries!

